Agent Alice On Computer
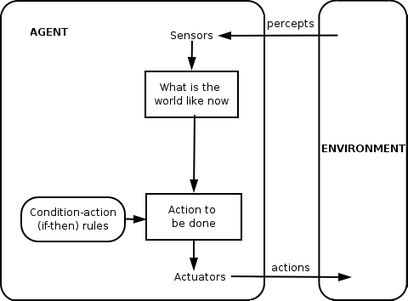
In computer science, a software agent is a computer program that acts for a user or other program in a relationship of agency, which derives from the Latin agere (to do): an agreement to act on one's behalf. Such 'action on behalf of' implies the authority to decide which, if any, action is appropriate.[1][2] Agents are colloquially known as bots, from robot. They may be embodied, as when execution is paired with a robot body, or as software such as a chatbotexecuting on a phone (e.g. Siri) or other computing device. Software agents may be autonomous or work together with other agents or people. Software agents interacting with people (e.g. chatbots, human-robot interaction environments) may possess human-like qualities such as natural language understanding and speech, personality or embody humanoid form (see Asimo).
Related and derived concepts include intelligent agents (in particular exhibiting some aspects of artificial intelligence, such as reasoning), autonomous agents (capable of modifying the methods of achieving their objectives), distributed agents (being executed on physically distinct computers), multi-agent systems (distributed agents that work together to achieve an objective that could not be accomplished by a single agent acting alone), and mobile agents (agents that can relocate their execution onto different processors).
Concepts[edit]
The basic attributes of an autonomous software agent are that agents
PLEASE NOTE: Agent Alice is free to play, but you can also purchase some items within the game for real money. If you don't want to use this feature, just disable in-app purchases on your device. Download today and join Agent Alice in a brand-new adventure mystery every week!
- are not strictly invoked for a task, but activate themselves,
- may reside in wait status on a host, perceiving context,
- may get to run status on a host upon starting conditions,
- do not require interaction of user,
- may invoke other tasks including communication.
The term 'agent' describes a software abstraction, an idea, or a concept, similar to OOP terms such as methods, functions, and objects.[citation needed] The concept of an agent provides a convenient and powerful way to describe a complex software entity that is capable of acting with a certain degree of autonomy in order to accomplish tasks on behalf of its host. But unlike objects, which are defined in terms of methods and attributes, an agent is defined in terms of its behavior[3][citation needed].
Various authors have proposed different definitions of agents, these commonly include concepts such as
- persistence (code is not executed on demand but runs continuously and decides for itself when it should perform some activity)
- autonomy (agents have capabilities of task selection, prioritization, goal-directed behavior, decision-making without human intervention)
- social ability (agents are able to engage other components through some sort of communication and coordination, they may collaborate on a task)
- reactivity (agents perceive the context in which they operate and react to it appropriately).
Distinguishing agents from programs[edit]
All agents are programs, but not all programs are agents.Contrasting the term with related concepts may help clarify its meaning. Franklin & Graesser (1997)[4] discuss four key notions that distinguish agents from arbitrary programs: reaction to the environment, autonomy, goal-orientation and persistence. Baldr sky zero.
Intuitive distinguishing agents from objects[edit]
- Agents are more autonomous than objects.
- Agents have flexible behaviour: reactive, proactive, social.
- Agents have at least one thread of control but may have more.[5]
Distinguishing agents from expert systems[edit]
- Expert systems are not coupled to their environment.
- Expert systems are not designed for reactive, proactive behavior.
- Expert systems do not consider social ability.[5]
Distinguishing intelligent software agents from intelligent agents in AI[edit]
- Intelligent agents (also known as rational agents) are not just computer programs: they may also be machines, human beings, communities of human beings (such as firms) or anything that is capable of goal-directed behavior.
- (Russell & Norvig 2003) harv error: no target: CITEREFRussellNorvig2003 (help)
Impact of software agents[edit]
Software agents may offer various benefits to their end users by automating complex or repetitive tasks.[6] However, there are organizational and cultural impacts of this technology that need to be considered prior to implementing software agents.
Organizational impact[edit]
Work contentment and job satisfaction impact[edit]
People like to perform easy tasks providing the sensation of success unless the repetition of the simple tasking is affecting the overall output. In general implementing software agents to perform administrative requirements provides a substantial increase in work contentment, as administering their own work does never please the worker. The effort freed up serves for a higher degree of engagement in the substantial tasks of individual work. Hence, software agents may provide the basics to implement self-controlled work, relieved from hierarchical controls and interference.[7] Such conditions may be secured by application of software agents for required formal support.
Cultural impact[edit]
The cultural effects of the implementation of software agents include trust affliction, skills erosion, privacy attrition and social detachment. Some users may not feel entirely comfortable fully delegating important tasks to software applications. Those who start relying solely on intelligent agents may lose important skills, for example, relating to information literacy. In order to act on a user's behalf, a software agent needs to have a complete understanding of a user's profile, including his/her personal preferences. This, in turn, may lead to unpredictable privacy issues. When users start relying on their software agents more, especially for communication activities, they may lose contact with other human users and look at the world with the eyes of their agents. These consequences are what agent researchers and users must consider when dealing with intelligent agent technologies.[8]
History[edit]
The concept of an agent can be traced back to Hewitt's Actor Model (Hewitt, 1977) - 'A self-contained, interactive and concurrently-executing object, possessing internal state and communication capability.'
To be more academic, software agent systems are a direct evolution of Multi-Agent Systems (MAS). MAS evolved from Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI), Distributed Problem Solving (DPS) and Parallel AI (PAI), thus inheriting all characteristics (good and bad) from DAI and AI.
John Sculley’s 1987 “Knowledge Navigator” video portrayed an image of a relationship between end-users and agents. Being an ideal first, this field experienced a series of unsuccessful top-down implementations, instead of a piece-by-piece, bottom-up approach. The range of agent types is now (from 1990) broad: WWW, search engines, etc.
Examples of intelligent software agents[edit]
Buyer agents (shopping bots)[edit]
Buyer agents[9] travel around a network (e.g. the internet) retrieving information about goods and services. These agents, also known as 'shopping bots', work very efficiently for commodity products such as CDs, books, electronic components, and other one-size-fits-all products. Buyer agents are typically optimized to allow for digital payment services used in e-commerce and traditional businesses.[10]
User agents (personal agents)[edit]
User agents, or personal agents, are intelligent agents that take action on your behalf. In this category belong those intelligent agents that already perform, or will shortly perform, the following tasks:
- Check your e-mail, sort it according to the user's order of preference, and alert you when important emails arrive.
- Play computer games as your opponent or patrol game areas for you.
- Assemble customized news reports for you. There are several versions of these, including CNN.
- Find information for you on the subject of your choice.
- Fill out forms on the Web automatically for you, storing your information for future reference
- Scan Web pages looking for and highlighting text that constitutes the 'important' part of the information there
- Discuss topics with you ranging from your deepest fears to sports
- Facilitate with online job ≤search duties by scanning known job boards and sending the resume to opportunities who meet the desired criteria
- Profile synchronization across heterogeneous social networks
Monitoring-and-surveillance (predictive) agents[edit]
Monitoring and Surveillance Agents are used to observe and report on equipment, usually computer systems. The agents may keep track of company inventory levels, observe competitors' prices and relay them back to the company, watch stock manipulation by insider trading and rumors, etc.
For example, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory has an agent that monitors inventory, planning, schedules equipment orders to keep costs down, and manages food storage facilities. These agents usually monitor complex computer networks that can keep track of the configuration of each computer connected to the network.
A special case of Monitoring-and-Surveillance agents are organizations of agents used to emulate the Human Decision-Making process during tactical operations. The agents monitor the status of assets (ammunition, weapons available, platforms for transport, etc.) and receive Goals (Missions) from higher level agents. The Agents then pursue the Goals with the Assets at hand, minimizing expenditure of the Assets while maximizing Goal Attainment. (See Popplewell, 'Agents and Applicability')
Data-mining agents[edit]
This agent uses information technology to find trends and patterns in an abundance of information from many different sources. The user can sort through this information in order to find whatever information they are seeking.
A data mining agent operates in a data warehouse discovering information. A 'data warehouse' brings together information from lots of different sources. 'Data mining' is the process of looking through the data warehouse to find information that you can use to take action, such as ways to increase sales or keep customers who are considering defecting.
'Classification' is one of the most common types of data mining, which finds patterns in information and categorizes them into different classes. Data mining agents can also detect major shifts in trends or a key indicator and can detect the presence of new information and alert you to it. For example, the agent may detect a decline in the construction industry for an economy; based on this relayed information construction companies will be able to make intelligent decisions regarding the hiring/firing of employees or the purchase/lease of equipment in order to best suit their firm.
Networking and communicating agents[edit]
Some other examples of current intelligent agents include some spam filters, game bots, and server monitoring tools. Search engine indexing bots also qualify as intelligent agents.
- User agent - for browsing the World Wide Web
- Mail transfer agent - For serving E-mail, such as Microsoft Outlook. Why? It communicates with the POP3 mail server, without users having to understand POP3 command protocols. It even has rule sets that filter mail for the user, thus sparing them the trouble of having to do it themselves.
- SNMP agent
- In Unix-style networking servers, httpd is an HTTP daemon that implements the Hypertext Transfer Protocol at the root of the World Wide Web
- Management agents used to manage telecom devices
- Crowd simulation for safety planning or 3D computer graphics,
- Wireless beaconing agent is a simple process hosted single tasking entity for implementing wireless lock or electronic leash in conjunction with more complex software agents hosted e.g. on wireless receivers.
- Use of autonomous agents (deliberately equipped with noise) to optimize coordination in groups online.[11]
Software development agents (aka software bots)[edit]
Software bots are becoming important in software engineering.[12] An example of a software bot is a bot that automatically repairs continuous integration build failures.[13]
Design issues[edit]
Issues to consider in the development of agent-based systems include
- how tasks are scheduled and how synchronization of tasks is achieved
- how tasks are prioritized by agents
- how agents can collaborate, or recruit resources,
- how agents can be re-instantiated in different environments, and how their internal state can be stored,
- how the environment will be probed and how a change of environment leads to behavioral changes of the agents
- how messaging and communication can be achieved,
- what hierarchies of agents are useful (e.g. task execution agents, scheduling agents, resource providers ..).
For software agents to work together efficiently they must share semantics of their data elements. This can be done by having computer systems publish their metadata.
The definition of agent processing can be approached from two interrelated directions:
- internal state processing and ontologies for representing knowledge
- interaction protocols – standards for specifying communication of tasks
Agent systems are used to model real-world systems with concurrency or parallel processing.
- Agent Machinery – Engines of various kinds, which support the varying degrees of intelligence
- Agent Content – Data employed by the machinery in Reasoning and Learning
- Agent Access – Methods to enable the machinery to perceive content and perform actions as outcomes of Reasoning
- Agent Security – Concerns related to distributed computing, augmented by a few special concerns related to agents
The agent uses its access methods to go out into local and remote databases to forage for content. These access methods may include setting up news stream delivery to the agent, or retrieval from bulletin boards, or using a spider to walk the Web. The content that is retrieved in this way is probably already partially filtered – by the selection of the newsfeed or the databases that are searched. The agent next may use its detailed searching or language-processing machinery to extract keywords or signatures from the body of the content that has been received or retrieved. This abstracted content (or event) is then passed to the agent's Reasoning or inferencing machinery in order to decide what to do with the new content. This process combines the event content with the rule-based or knowledge content provided by the user. If this process finds a good hit or match in the new content, the agent may use another piece of its machinery to do a more detailed search on the content. Finally, the agent may decide to take an action based on the new content; for example, to notify the user that an important event has occurred. This action is verified by a security function and then given the authority of the user. The agent makes use of a user-access method to deliver that message to the user. If the user confirms that the event is important by acting quickly on the notification, the agent may also employ its learning machinery to increase its weighting for this kind of event.
Bots can act on behalf of their creators to do good as well as bad. There are a few ways which bots can be created to demonstrate that they are designed with the best intention and are not built to do harm. This is first done by having a bot identify itself in the user-agent HTTP header when communicating with a site. The source IP address must also be validated to establish itself as legitimate. Next, the bot must also always respect a site's robots.txt file since it has become the standard across most of the web. And like respecting the robots.txt file, bots should shy away from being too aggressive and respect any crawl delay instructions.[14]
Notions and frameworks for agents[edit]
- DAML (DARPA Agent Markup Language)
- 3APL (Artificial Autonomous Agents Programming Language)
- Web Ontology Language (OWL)
- daemons in Unix-like systems.
- Java Agent Template (JAT)
- Java Agent Development Framework (JADE)
- SARL agent programming language (arguably an Actor and not Agent oriented paradigm)

See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Nwana, H. S. (1996). 'Software Agents: An Overview'. Knowledge Engineering Review. 21 (3): 205–244. CiteSeerX10.1.1.50.660. doi:10.1017/s026988890000789x.
- ^Schermer, B. W. (2007). Software agents, surveillance, and the right to privacy: A legislative framework for agent-enabled surveillance(paperback). 21. Leiden University Press. pp. 140, 205–244. hdl:1887/11951. ISBN978-0-596-00712-6. Retrieved 2012-10-30.
- ^Wooldridge, M.; Jennings, N. R. (1995). 'Intelligent agents: theory and practice'. 10 (2). Knowledge Engineering Review: 115–152.Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^Franklin, S.; Graesser, A. (1996). 'Is it an Agent, or just a Program?: A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents'. Intelligent Agents III Agent Theories, Architectures, and Languages. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1193. University of Memphis, Institute for Intelligent Systems. pp. 21–35. doi:10.1007/BFb0013570. ISBN978-3-540-62507-0.
- ^ abWooldridge, Michael J. (2002). An Introduction to Multiagent Systems. New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 27. ISBN978-0-471-49691-5.
- ^Serenko, A.; Detlor, B. (2004). 'Intelligent agents as innovations'(PDF). 18 (4): 364–381.Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^Adonisi, M. (2003). 'The relationship between Corporate Entrepreneurship, Market Orientation, Organisational Flexibility and Job satisfaction'(PDF) (Diss.). Fac.of Econ.and Mgmt.Sci., Univ.of Pretoria.Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^Serenko, A.; Ruhi, U.; Cocosila, M. (2007). 'Unplanned effects of intelligent agents on Internet use: Social Informatics approach'(PDF). 21 (1–2). Artificial Intelligence & Society: 141–166.Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^Haag, Stephen (2006). 'Management Information Systems for the Information Age': 224–228.Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^'Maximize Your Business Impact How to Use Facebook Chatbots'. Keystone Click. 2016-08-26. Retrieved 2017-09-07.
- ^Shirado, Hirokazu; Christakis, Nicholas A (2017). 'Locally noisy autonomous agents improve global human coordination in network experiments'. Nature. 545 (7654): 370–374. Bibcode:2017Natur.545.370S. doi:10.1038/nature22332. PMC5912653. PMID28516927.
- ^Lebeuf, Carlene; Storey, Margaret-Anne; Zagalsky, Alexey (2018). 'Software Bots'. IEEE Software. 35: 18–23. doi:10.1109/MS.2017.4541027.
- ^Urli, Simon; Yu, Zhongxing; Seinturier, Lionel; Monperrus, Martin (2018). 'How to design a program repair bot? Insights from the Repairnator Project'. Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Software Engineering Software Engineering in Practice - ICSE-SEIP '18. pp. 95–104. arXiv:1811.09852. doi:10.1145/3183519.3183540. ISBN9781450356596.
- ^'How to Live by the Code of Good Bots'. DARKReading from Information World. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
External links[edit]
- Software Agents: An Overview, Hyacinth S. Nwana. Knowledge Engineering Review, 11(3):1–40, September 1996. Cambridge University Press.
- FIPA The Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agents
- JADE Java Agent Developing Framework, an Open Source framework developed by Telecom Italia Labs
- SemanticAgent An Open Source framework to develop SWRL based Agents on top of JADE
- Mobile-C A Multi-Agent Platform for Mobile C/C++ Agents.
- HLL High-Level Logic (HLL) Open Source Project.
- Open source project KATO for PHP and Java developers to write software agents
Play Mobile games on PC with Andy Android Emulator
Wooga takes you back in a bizarre voyage from the 1960s as the fearless Agent Alice! The very compelling storyline is like coming straight from a mystery novel. You will be visiting strange places every week to uncover the hidden clues. Every time there are new discoveries, Oberon’s evil plans start to crumble. Watch out for weekly episodes and be ready for suspense as you keep an eye on the puzzles, romance and adventure all wrapped up in a mysterious hidden-object-game. Download Agent Alice for PC and find out the pieces of the riddle in no time.
Hard-core beginning
Agent Alice’s uncanny gameplay opens up every scene where there are scattered stuffs all-over. You need to pick the objects from your list to earn points to multiply as you do things swiftly. This will eventually lead to gain stars so that the story would move forward. Perhaps the stop-and-go element of the story makes every one get hooked on Alice, Ben and Pete’s mysterious adventure. Alice is very determined by nature and would do whatever it takes to solve the puzzles. Ben is always keen on seeking for justice while Pete is your typical charmer who’s out to steal Alice’s heart foolishly.
One of the main areas updated in the North American version was the NHL and the new rules including the salary cap. NHL Eastside Hockey Manager 2005 Free Download.NHL Eastside Hockey Manager 2005 Free Download PC GameClick on below button to start NHL Eastside Hockey Manager 2005 Download Free PC Game. This version included new rules for all the featured leagues based on the 2005–06 hockey season. Nhl hockey news. At the same time, SI Games made available a free season update for the European version of the game, which update the earlier release with the new rules and data included in the North American release version.
Time waits for no one
Unfolding the peak of the story sometimes lets you wait an hour or so to keep you anticipating. Some new episodes entail you to wait longer for the same reason. That should be enough time to work on your desktop for your other assignments. What better way to do this than to have Agent Alice on PC so that no more precious time is wasted. Andy’s emulating software lets you put all your favourite game, social media and instant messaging apps in one place. This will also clear up the clutter on your desk so you don’t have to juggle between different devices.
Search the valleys and the hills
Agent Alice is an astonishing creation for iOS and Android and is probably the best hidden-object-game you could come across. The plot is huddled in a mystery murder that occurred inside the theatre after an outstanding performance. As it turns out, Ms Alice Wallace happens to be the most celebrated detective during the swinging ‘60s. Let’s see what her job really is in the game’s highlights so you know what needs to be done after you download Agent Alice for PC.
- Search the stage for objects on the list. Watch the mysteries unfold in full HD and superb sound effects that’s enough to give you the chills. Andy is backed up with virtual optimisation feature and all you need is a good graphics card to make it work.
- Tap whatever mystery you uncovered. If you are working at considerable distance from the computer, take advantage of Andy’s virtual joystick feature and use your smartphone to control the game.
- No games are the same so that means, new plots and mechanics await every now and then. Perhaps mystery spices things up! Several dialogues appear and you have to reply with the intriguing set of answers provided. Your choice would basically run what happens next in the story.
- Mini-games come up to keep you at the edge of your seats. It adds a bit of excitement to keep you entertained but that’s just half the story. New puzzle styles goes with the updates and new episodes every week so there’s so much to hang onto and to see here. Google Play Store updates are seamlessly carried over to your desktop as it goes with the many features of Andy.
Andy for Agent Alice
There’s always a new culprit who’s out and on the loose to create trouble. Join Alice and her team to help unlock a new mystery and solve the case. Your quick intuition has to be pretty intense in spotting the difference, matching the objects and picking the right lock and key. Do you have what it takes to catch the felon in this highly climactic gameplay? Download Agent Alice for PC and step into the action! We have provided a trail on the easy steps to enhance your virtual life. Check out the links that goes with the instructions after this.
How to Download Agent Alice for PC:
Step 1: Download the android emulator software Andy and it is available for free. Click here to download: Download
Step 2: Start the installation of Andy by clicking on the installer file you downloaded.
Step 3: When the software is ready to be used, start it and complete the sign up procedure and login with Google Play account.
Step 4: Start Google play store app and use its search tool to search Agent Alice download.
Step 5: Find Agent Alice and start the installation.
Step 6: Launch the game and you can now play Agent Alice on pc using a mouse or your keyboard and even your touch screen, you can use the control button to emulate the pinch function to zoom in and out.
Step 7: You can also install remote control app form here for remotely accessing the game: Andy remote control app
Support: we maintain an online real-time Facebook support group if you have any issues with Andy OS to the installation process, You can use this link to access the group: support
Enjoy Playing Agent Alice on PC!!!